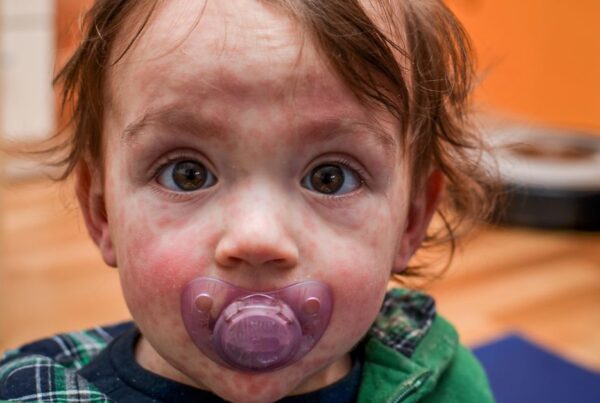
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD) is an uncomfortable and contagious viral infection that results in a painful rash on the hands and soles of the feet and inside the mouth and throat. It is most common in children under 10; however, people of any age can become infected. This article covers the signs and symptoms of HFMD, the natural treatment of HFMD for all ages, and when to see a doctor.
What Is Hand-Foot-And-Mouth Disease?
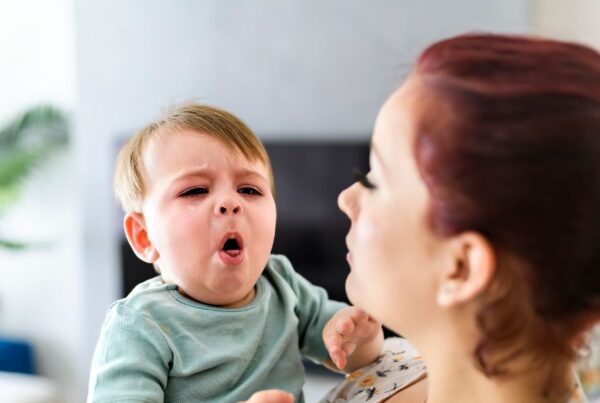
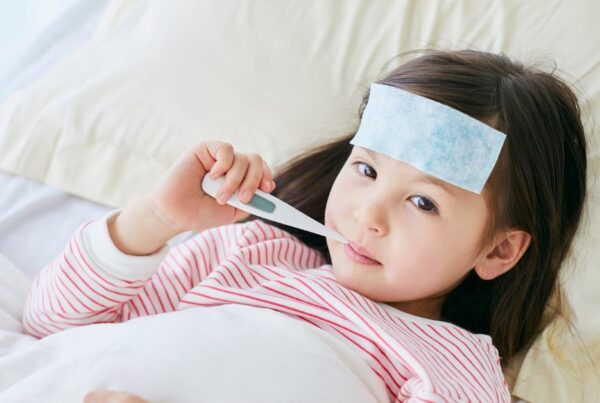
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease is a viral infection that results in a characteristic rash on the palms of hands and soles of feet, plus small, painful mouth and throat ulcers. In some cases, the rash can also spread to the buttocks, genitals, elbows, and legs. The rash is usually red and flat or it may be vesicular (small blisters). A low-grade fever often accompanies HFMD. The illness usually resolves within 7-10 days.
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease is caused by a handful of different human enteroviruses and coxsackieviruses. The most common culprits are coxsackievirus A16, coxsackievirus A6, and human enterovirus A71. These viruses are spread through contact with body fluids, feces, and blisters. The virus can live on surfaces, so cleaning, handwashing, and overall good hygiene are extremely important in halting the spread of HFMD.
The incubation period for the virus is usually 3-6 days. Symptoms start with a sore throat and a general feeling of being unwell and then progress after several days to the development of a rash. People may transmit the virus before symptoms appear. Because the virus lives in the gut, it may be shed in the stools for weeks after symptoms resolve.
In some rare cases, hand-foot-and-mouth disease can cause a child’s fingernails and/or toenails to fall off approximately a month after having the disease. Though this may look alarming, it is harmless and nails will grow back.
Integrative Treatment Of Hand-Foot-And-Mouth Disease
The treatment of hand-foot-and-mouth disease focuses on providing comfort, boosting the immune system, managing fever, preventing dehydration, and administering antiviral herbal remedies.
Pain Relief For Hand-Foot-And-Mouth Disease
The discomfort associated with hand-foot-and-mouth disease can range from mild to severe. When discomfort causes significant distress, pain relief can be the most important part of HFMD management. Words cannot fully convey how heart-wrenching and exhausting it is to look after little ones experiencing pain or discomfort that prevents them from eating, sleeping, drinking, or playing like they usually would.
Soothing herbal drinks can be helpful for pain. Usually, these will need to be served cooler than usual because hot drinks may be uncomfortable to swallow. Lemon balm tea is my favorite because it is delicious, antiviral, and pain-relieving. Lemon balm is safe for all ages and for pregnant and breastfeeding women. Honey is also soothing and can be added for kids over 2.
Botanical salves that contain pain-relieving essential oils like calendula, lavender, and frankincense can be helpful for relief. I prefer Henry’s Healing Salve from Henry’s Homestead. If you’re breastfeeding, the topical application of breast milk to lesions may help with healing and pain.
If pain is getting in the way of eating, drinking, or sleeping, and herbal treatment isn’t enough to provide relief, then using conventional pain medications like ibuprofen and acetaminophen is advised. Though these medications come with side effects, they are usually safe when used as directed for a short amount of time. Eating, sleeping, and staying hydrated are essential for efficient healing from viral infections.
Read more: Should I Take Tylenol Or Ibuprofen Or Aspirin? – Dr. Green Mom.
Immune Boosting Vitamins For Hand-Foot-And-Mouth Disease
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease is healed by the body’s immune system. Though it will generally resolve itself within 7-10 days without treatment, boosting the immune system may help to more quickly relieve symptoms.
Vitamin A is an important nutrient for the immune system, particularly for fighting viral infections. Research has shown that vitamin A deficiency is associated with more severe HFMD in children.
Vitamin D is another important immunity nutrient and research has shown that vitamin D deficiency is associated with more severe HFMD in children.
Vitamins A & D can be taken as single supplements or can be obtained through whole-food supplements like cod liver oil or beef liver capsules.
In my practice, I often have patients on a daily multivitamin, cod liver oil, or beef liver supplement to provide immune-boosting nutrients as a preventative. Consequently, my patients usually have enough vitamins A and D to fight the infection, and I can focus my treatment efforts elsewhere. However, if kids don’t regularly get vitamins A and D through diet, supplementation, and lifestyle, then I consider these an important part of HFMD treatment. I also include these vitamins in my treatment plans anytime the symptoms are severe.
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin and care must be taken not to overdose. This is especially important during pregnancy because high doses of vitamin A can lead to birth defects.
Read more about safe doses of vitamin A: Benefits of Vitamin A + Pediatric Dosing – Dr. Green Mom.
Probiotics For Treatment And Prevention Of Hand-Foot-And-Mouth Disease
The gut microbiome plays an important role in susceptibility to enteroviruses in general. A robust and diverse microbiome is more resistant to infection. Research is still in its infancy, but there is emerging evidence that probiotics may be able to reduce the spread of HFMD, prevent gut dysbiosis after HFMD, and reduce the symptoms of HFMD. To take advantage of the benefits of probiotics for preventing and treating HFMD, incorporate them into your daily routine.
Fever Management For Low Grade Fevers
The fever that accompanies hand-foot-and-mouth disease is generally low-grade and doesn’t require intervention. If the fever is uncomfortable, drinking herbal teas can help.
Read more: Fever Management Herbal Teas Safe in Childhood – Dr. Green Mom.
Preventing Dehydration
Dehydration is one of the most common complications of hand-foot-and-mouth disease. That’s because fever and blisters can increase fluid loss while the presence of mouth and throat ulcers may make drinking painful.
One of the best ways to counter dehydration is to offer popsicles or ice cubes because the coldness can help soothe the pain. Some ice cube options include frozen herbal teas, coconut water, yogurt, bone broth, or my homemade electrolyte drink.
Read more information about the signs of dehydration: Signs of Dehydration & Homemade Electrolyte Drink Recipe – Dr. Green Mom.
Herbal Antiviral Treatment For Hand-Foot-And-Mouth Disease
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease can be treated with antiviral herbs in the hopes of speeding recovery. Though research is sparse, there is a long history of herbal treatment among herbalists, naturopathic doctors, and natural-health-minded parents.
Elderberry is my top choice. It has potent antiviral and immune system benefits. It hasn’t yet been studied as a treatment for HFMD, but some research shows that elderberry phytochemicals like quercetin and other flavonoids are effective against the viruses that cause HFMD.
Ganoderma, aka reishi, is a medicinal mushroom that has been studied as a potential treatment for hand-foot-and-mouth disease and shows promising antiviral effects.
Licorice is another favorite HFMD treatment of mine. It is a good antiviral and works well to soothe the pain of sore throats. I prefer licorice as a pastille, glycerite, or tea (remember to let it cool). Licorice isn’t my first choice during pregnancy because there is some evidence that it may cause problems.
Gut Dysbiosis After Hand-Foot-And-Mouth Disease
Because HFMD is an intestinal virus, it may disrupt the intestinal microbiome. Some people may benefit from a gut healing protocol after recovering from HFMD.
Read more: How To Heal The Gut (For Kids) – Dr. Green Mom.
When To Seek Medical Attention
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease is usually mild and most children recover at home. However, there are some scenarios in which you should seek medical care.
See a healthcare provider if your child is experiencing severe symptoms, if they seem unresponsive or confused, and/or if they are in too much pain to drink and are in danger of dehydration.
You should also see a healthcare provider if your child is immunocompromised, if they are experiencing a prolonged fever (more than 3 days), or if their symptoms don’t resolve within 10 days.
Babies under 6 months with HFMD should be seen by a healthcare provider, even if symptoms seem mild.
Summary
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD) is a common and contagious viral infection that usually affects kids under 10. It causes a characteristic rash on the hands, feet, and inside the mouth, but it can also spread to other locations like the buttocks, elbows, and legs. Treatment is aimed at relieving pain, maintaining hydration, boosting the immune system, and fighting the infection. Symptoms usually resolve within 7-10 days.
References:
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease | CDC
Saguil, A., Kane, S. F., Lauters, R., & Mercado, M. G. (2019). Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease: Rapid Evidence Review. American family physician, 100(7), 408–414.
Kimmis, B. D., Downing, C., & Tyring, S. (2018). Hand-foot-and-mouth disease caused by coxsackievirus A6 on the rise. Cutis, 102(5), 353–356.
Bian, L., Gao, F., Mao, Q., Sun, S., Wu, X., Liu, S., Yang, X., & Liang, Z. (2019). Hand, foot, and mouth disease associated with coxsackievirus A10: more serious than it seems. Expert review of anti-infective therapy, 17(4), 233–242. https://doi.org/10.1080/14787210.2019.1585242
Giachè, S., Borchi, B., Zammarchi, L., Colao, M. G., Ciccone, N., Sterrantino, G., Rossolini, G. M., Bartoloni, A., & Trotta, M. (2021). Hand, foot, and mouth disease in pregnancy: 7 years Tuscan experience and literature review. The journal of maternal-fetal & neonatal medicine : the official journal of the European Association of Perinatal Medicine, the Federation of Asia and Oceania Perinatal Societies, the International Society of Perinatal Obstetricians, 34(9), 1494–1500. https://doi.org/10.1080/14767058.2019.1638898
Li, Y. P., Wang, M. Q., Deng, H. L., Li, M., Zhang, X., Dang, S. S., & Zhai, S. (2020). Association of polymorphisms in the vitamin D receptor gene with susceptibility to and severity of hand, foot, and mouth disease caused by coxsackievirus A16. Journal of medical virology, 92(3), 271–278. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25603
Jin, Y. J., Han, X., & Ge, G. L. (2020). Zhongguo zhen jiu = Chinese acupuncture & moxibustion, 40(4), 391–394. https://doi.org/10.13703/j.0255-2930.20190820-k0001
Li, Y. P., Deng, H. L., Xu, L. H., Wang, M. Q., Li, M., Zhang, X., & Dang, S. S. (2019). Association of polymorphisms in the vitamin D receptor gene with severity of hand, foot, and mouth disease caused by enterovirus 71. Journal of medical virology, 91(4), 598–605. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25349
Chen, S., Yang, Y., Yan, X., Chen, J., Yu, H., & Wang, W. (2012). Influence of vitamin A status on the antiviral immunity of children with hand, foot and mouth disease. Clinical nutrition (Edinburgh, Scotland), 31(4), 543–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2011.12.005
Li, Y. P., Deng, H. L., Wang, W. J., Wang, M. Q., Li, M., Zhang, Y. F., Wang, J., & Dang, S. S. (2020). Vitamin D receptor gene methylation in patients with hand, foot, and mouth disease caused by enterovirus 71. Archives of virology, 165(9), 1979–1985. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-020-04701-8
Dang, H. X., Liu, C. J., Li, J., Chen, S. J., & Xu, F. (2017). Clinical Significance and Prognostic Effect of Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D Concentrations in Critical and Severe Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease. Nutrients, 9(5), 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9050478
Richard S. A. (2021). Exploring the Pivotal Immunomodulatory and Anti-Inflammatory Potentials of Glycyrrhizic and Glycyrrhetinic Acids. Mediators of inflammation, 2021, 6699560. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6699560
Wang, J., Chen, X., Wang, W., Zhang, Y., Yang, Z., Jin, Y., Ge, H. M., Li, E., & Yang, G. (2013). Glycyrrhizic acid as the antiviral component of Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch. against coxsackievirus A16 and enterovirus 71 of hand foot and mouth disease. Journal of ethnopharmacology, 147(1), 114–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2013.02.017
Ang, W. X., Sarasvathy, S., Kuppusamy, U. R., Sabaratnam, V., Tan, S. H., Wong, K. T., Perera, D., & Ong, K. C. (2021). In vitro antiviral activity of medicinal mushroom Ganoderma neo-japonicum Imazeki against enteroviruses that caused hand, foot and mouth disease. Tropical biomedicine, 38(3), 239–247. https://doi.org/10.47665/tb.38.3.063
Zhang, W., Tao, J., Yang, X., Yang, Z., Zhang, L., Liu, H., Wu, K., & Wu, J. (2014). Antiviral effects of two Ganoderma lucidum triterpenoids against enterovirus 71 infection. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 449(3), 307–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.05.019
Yao, C., Xi, C., Hu, K., Gao, W., Cai, X., Qin, J., Lv, S., Du, C., & Wei, Y. (2018). Inhibition of enterovirus 71 replication and viral 3C protease by quercetin. Virology journal, 15(1), 116. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12985-018-1023-6
Dai, W., Bi, J., Li, F., Wang, S., Huang, X., Meng, X., Sun, B., Wang, D., Kong, W., Jiang, C., & Su, W. (2019). Antiviral Efficacy of Flavonoids against Enterovirus 71 Infection in Vitro and in Newborn Mice. Viruses, 11(7), 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11070625
Yan, S., Lu, Y., Zhang, G., Li, X., Wang, Z., Yao, C., Wu, G., Luo, L., Ai, Y., Guo, Z., Li, H., Li, T., Jia, Z., Wang, J., He, L., & Liu, B. (2020). Effect of heat-clearing and detoxifying Chinese medicines combined with conventional therapy on mild hand, foot, and mouth disease with fever: An individual patient data meta-analysis. Medicine, 99(23), e20473. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000020473
Sheng, Y., Liu, X., Wang, Q., Zhang, Y., Huang, L., Hu, D., Ren, P., Hong, Q., & Kang, D. (2022). Herbal Granules of Heat-Clearing and Detoxifying for Children with Mild Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis. Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM, 2022, 6818406. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/6818406
Chen, X., Wang, C., Xu, L., Chen, X., Wang, W., Yang, G., Tan, R. X., Li, E., & Jin, Y. (2013). A laboratory evaluation of medicinal herbs used in china for the treatment of hand, foot, and mouth disease. Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM, 2013, 504563. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/504563
Silva, G. L., Luft, C., Lunardelli, A., Amaral, R. H., Melo, D. A., Donadio, M. V., Nunes, F. B., de Azambuja, M. S., Santana, J. C., Moraes, C. M., Mello, R. O., Cassel, E., Pereira, M. A., & de Oliveira, J. R. (2015). Antioxidant, analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of lavender essential oil. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciencias, 87(2 Suppl), 1397–1408. https://doi.org/10.1590/0001-3765201520150056
Al-Harrasi, A., Ali, L., Hussain, J., Rehman, N. U., Mehjabeen, Ahmed, M., & Al-Rawahi, A. (2014). Analgesic effects of crude extracts and fractions of Omani frankincense obtained from traditional medicinal plant Boswellia sacra on animal models. Asian Pacific journal of tropical medicine, 7S1, S485–S490. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1995-7645(14)60279-0
De Angelis, C., Di Stadio, A., Vitale, S., Saccone, G., Angelis, M. C., Zizolfi, B., & Di Spiezio Sardo, A. (2022). Use of calendula ointment after episiotomy: a randomized clinical trial. The journal of maternal-fetal & neonatal medicine : the official journal of the European Association of Perinatal Medicine, the Federation of Asia and Oceania Perinatal Societies, the International Society of Perinatal Obstetricians, 35(10), 1860–1864. https://doi.org/10.1080/14767058.2020.1770219
Sinopoli, A., Caminada, S., Isonne, C., Santoro, M. M., & Baccolini, V. (2022). What Are the Effects of Vitamin A Oral Supplementation in the Prevention and Management of Viral Infections? A Systematic Review of Randomized Clinical Trials. Nutrients, 14(19), 4081. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14194081
Lin, H., Sun, L., Lin, J., He, J., Deng, A., Kang, M., Zeng, H., Ma, W., & Zhang, Y. (2014). Protective effect of exclusive breastfeeding against hand, foot and mouth disease. BMC infectious diseases, 14, 645. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-014-0645-6